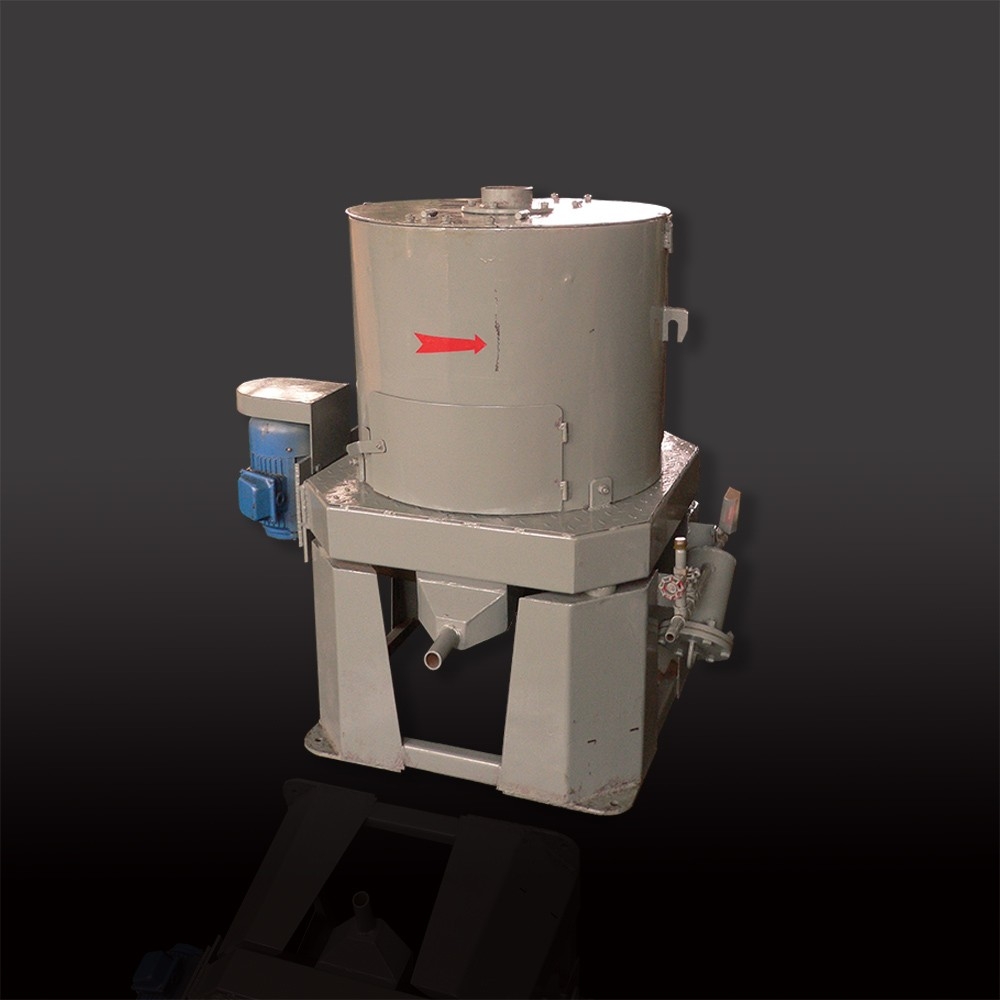
Centrifugal Gold Concentrator
GTEK STLB Centrifugal Concentrator can be used not only for placer gold mining, but also for hard rock mining to recover the free gold, replacing amalgamation.
Description
The first unit of batch Knelson Centrifugal Concentrator was introduced into the mineral processing industry in 1978. Knelson Centrifugal Concentrator has now been widely used in industrial gravity separation processes. Nelson Centrifugal Concentrator was first introduced as a semi-batch unit and has gone several iterations of design leading to the development of a continuous discharge machine. It has now almost an essential unit operation in any gold processing plant to assess the gravity recoverable gold content in the ore as well as to recovery fine free gold from the grinding circuit. GTEK STLB Centrifugal Concentrator can be used not only for placer gold mining, but also for hard rock mining to recover the free gold, replacing amalgamation.
Since 1985, several models of Centrifugal Concentator have been developed by GTEK. As more and more Centrifugal Concentrator were accept in gold industry and mineral processing, in order to find out how much gold can be extracted from an ore if a knelson concentrator is installed, a laboratory scale centrifugal concentrator was created by GTEK
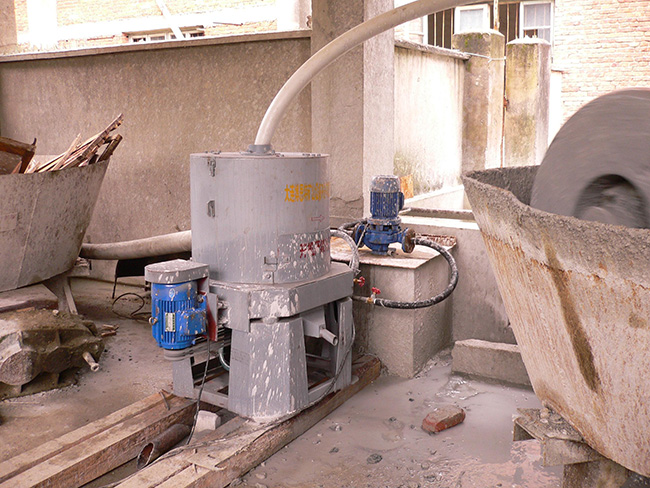
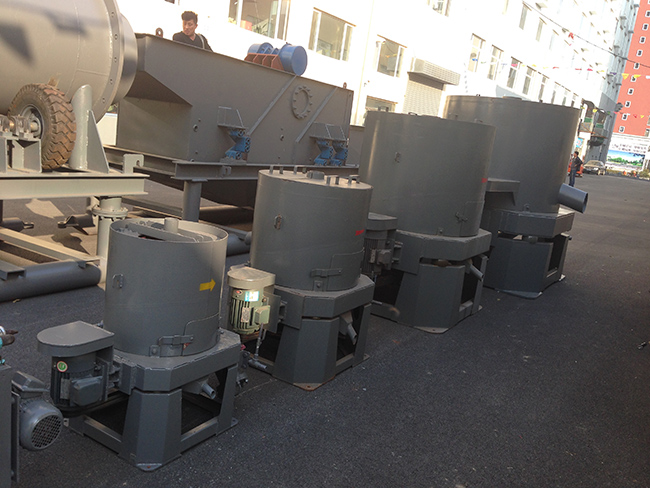



Working Principle
The key component of the centrifugal concentrator is a cone shaped concentrate bowl, rotated at a high speed by an electric motor and a pressurized water jacket encompassing the bowl. Feed slurry is introduced into through feed tube and into the concentrate cone. When the slurry reaches the bottom of the cone, it is forced outward and up the cone under the influence of centrifugal force.The slurry fills each groove to create a concentrating bed.The light particles are discharged continuously through a launder as tails, while the concentrate is kept inside the grooves of the inner bowl. Water is introduced through a series of fluidization holes in the inner bowl. This fluidization water force is expected to be strong enough to inhibit severe compaction of the heavy mineral bed due to the strong centrifugal force.
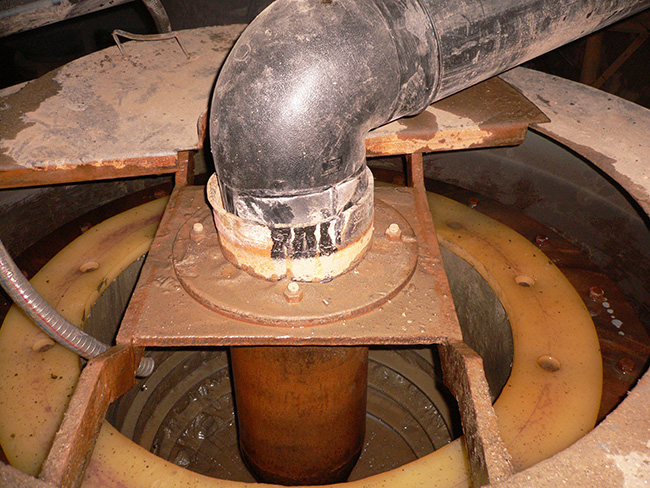
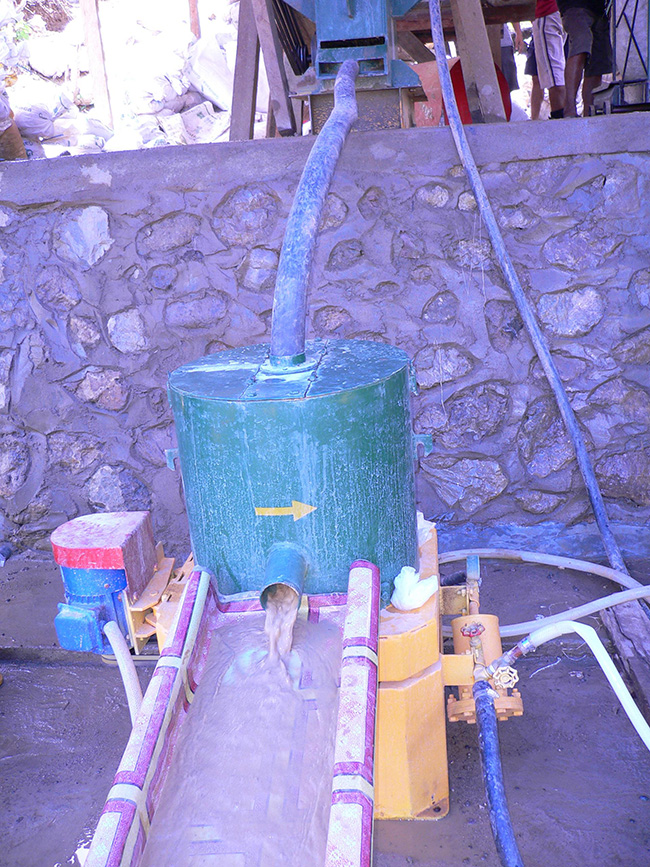
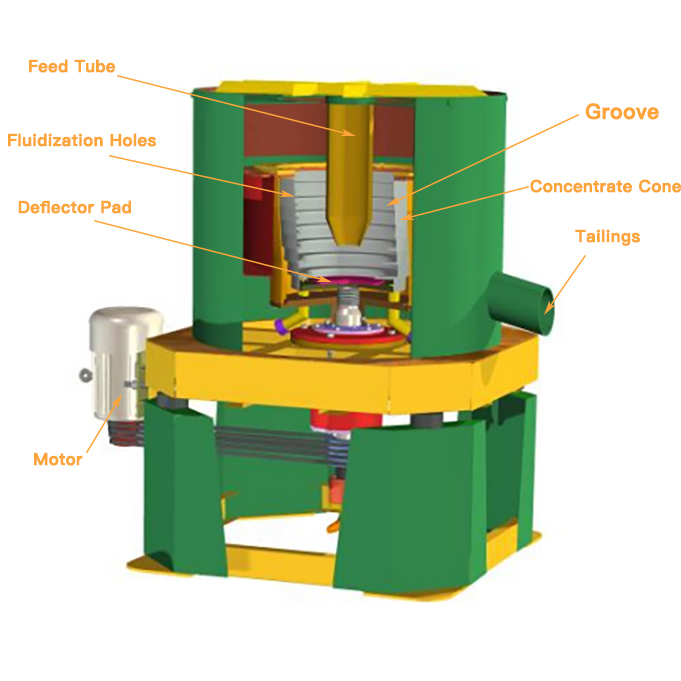


Features
1. Large throughout capacity treating a wide range size of material;
2. Yielding a high grade concentrate with small mess that could be easily smelted;
3. Unmatched recovery performance;
4. Environmentally friendly.
Model | Solids Feed Capacity (t/hr) | Fluidization Water Requirement (m³/hr) | Fluidization Water Pressure (Mpa) | Slurry With Water (m³/hr) | Feed Size (mm) | Concentration Cleaning Up Cycle | Concentrate Weight (Kg) | Power (kW) | Weight (kg) | Dimension (mm) | |||
Vein Gold | Placer Gold | L | W | H | |||||||||
LAB TYPE | 25kg~40kg | 0.5L~4L | 0.03~0.05 | 0.5L~4L | 0~1.7 (10mesh) | 1~3 hours | 2~6 hours | 100g~200g | 0.25 | 45 | 600 | 370 | 435 |
STLB20 | 0.2~0.5 | 0.8~1.0 | 0.03~0.05 | 0.5~1.0 | 0~2 | 1~2 | 0.75 | 205 | 1065 | 760 | 890 | ||
STLB30 | 2~3 | 3~4 | 0.03~0.05 | 2~3 | 0~3 | 5~8 | 1.2 | 450 | 1270 | 980 | 1205 | ||
STLB60 | 8~12 | 8~10 | 0.03~0.05 | 10~12 | 0~3 | 20~25 | 4 | 1100 | 1865 | 1440 | 1675 | ||
STLB80 | 30~40 | 20~30 | 0.03~0.05 | 30~40 | 0~3 | 40~50 | 11 | 2500 | 2520 | 1900 | 2020 | ||